“EUTHANASIA: Mercy Killing or Death with Dignity”
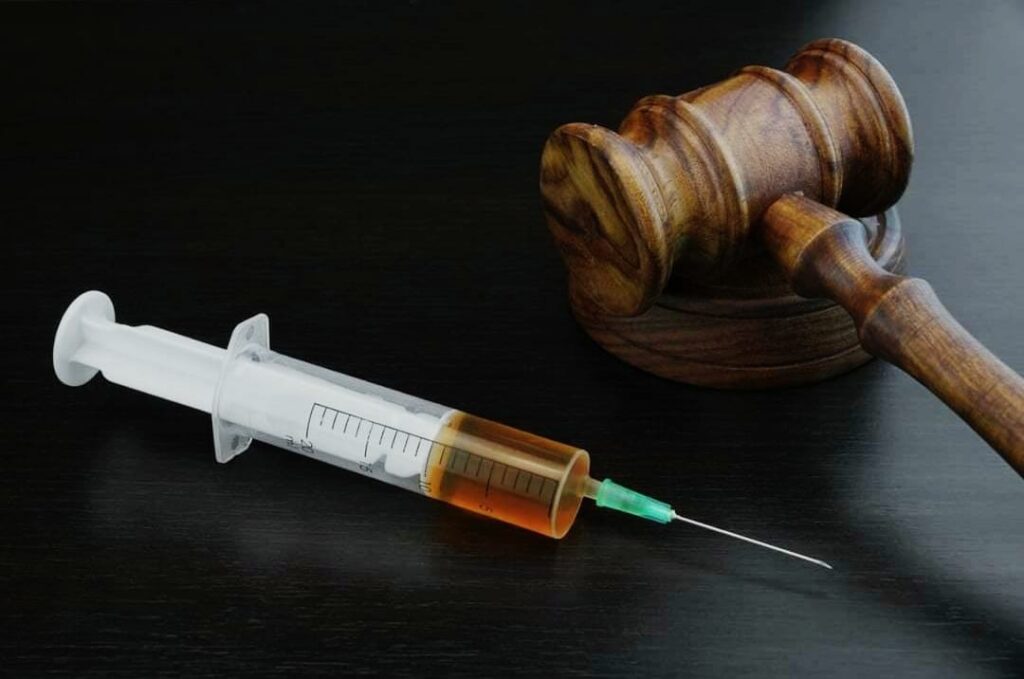
EUTHANASIA: Mercy Killing or Death with Dignity “Under Article 21” of the Indian Constitution- “No Person shall be deprived of his life and personal liberty except according to procedure establish by Law”, which means the State shall ensure good quality of life, livelihood, liberty and a dignified life. question as to whether the Right to Life includes the Right Not to Life or to Right to Die. Death can be defined as the Termination of life which means death which is causeda) Naturally b) Unnaturally. Further, it can be caused by the action as well as the inaction of a person. Causing the extinction of a life unnaturally by the action of oneself or someone else can be morally bad at the same time it is legally punishable. WHAT IS EUTHANASIA- Many a times life becomes very painful and unbearable so a man may wish death. This voluntary act of embracing death is known as Euthanasia or Mercy Killing or Dayamarana. DID IT EXISTED IN ANCIENT TIMES In Ancient India we find many types of voluntary death practices like Sati, Jauhars, Samadhi and Prayopaveshan (Starving to Death). According to John Locke a philosopher who stated that person have the Right to their Life, Liberty and Property which if termed as Absolute Right to Life then they must be given the Right to decide to die or to end their life in case of a terminal illness. “Naresh Marotrao Sakhre and Anrs. V/s. Union of India” the court observed the difference between Euthanasia and the suicide. Suicide was an act of self destruction to terminates one own life without the aid or assistance of any other human agency whereas euthanasia involves the intervention human agency to ends one’s life. “Gian Kaur V/s. State of Punjab” where it was held that Right to Life does not include Right to Die or Right to be killed. It was upheld that Right to Life was natural right embodied in Article 21 but suicide was unnatural termination for extinction of life and therefore incompatible and inconsistence with the concept of the Right to Life. “In Common Cause V/s. Union of India” where 5 judge bench of the Supreme Court recognized and gave sanction to Passive Euthanasia and living will/ advance directives. The implication of this was Right to Die with dignity is now a fundamental right. “In Aruna Shanbaug V/s. Union of India.” In this case how was a nurse spending over 41 years in a vegetative state as a result of Sexual-Assault, the Supreme Court of India responded to the plea to Euthanasia wherein although the court rejected the petition but allowed Passive Euthanasia in India. The Guidelines in the Passive Euthanasia is the decision to withdraw treatment, nutrition or water established that the decision to discontinue life support must be taken by Parents, Spouse or other Close Relative, or in the absence of them, by a “Next Friend”. The decision also requires court approval. ACTIVE EUTHANASIA Active Euthanasia is when a professional or another person intentionally causes a patient to die. For example, by injecting the patient by a lethal dose of a drug. PASSIVE EUTHANASIA Passive Euthanasia intentionally letting a patient die by withholding the artificial life support such as a ventilator or a feeding tube. The prima-facie distinction between active and passive euthanasia is that the former involves killing a patient while the later involves letting a patient to die. ADVANTAGES & DISADVANTAGES OF EUTHANASIA ADVANTAGE OF EUTHANASIA 1. It is a way to end an extremely miserable and painful life. 2. The Family member of the dying patient is relived of the physical, emotional, economical and mental stress. 3. The patients also have a right to refuse medical treatment. 4. It will free up medical fund of the state to help other poor and needy people. 5. It is the exercise of the fundamental right. DISADVANTAGE OF EUTHANASIA 1. Commercialization of euthanasia can take place. 2. The poor people can resort to this in order to avoid pecuniary difficulties of medication. 3. Old and destitute who are considered as burden on other people can make use of this to shelve their responsibilities. 4. It will de-value Human dignity and offend the Principal of sanctity of life. CONCLUSION For those who are facing terminal illness who are in irremediable pain and suffering, wish to exercise their right to die with dignity, a system of course should be available to them. – MAMTA SINGH SHUKLA (ADVOCATE DELHI HIGH COURT) MOBILE – 9560044035 Email Id: adv.mamtasinghshukla@gmail.com
Right to Privacy as Fundamental Right

Right to Privacy as Fundamental Right The Supreme Court of India in the case of Justice K.S Putta Swammy Vs. Union of India 2017 had declared the Right to Privacy as Fundamental Right under the Constitution of India DATA PROTECTION Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act 2023): Data protection is the process of safeguarding important information from corruption, compromise or loss. Data is the large collection of information that is stored in a computer or on a network. The importance of data protection increases as the amount of data created and stored continues to grow at unprecedented rates. DPDP Act set nationwide standards for the handling of all types of Personal Data- “Any Data about an individual’s who is identifiable by or in relation to such data”. This includes data like an individual’s names, Phone Number and Aadhar details. It is a part of worldwide trend of Government regulating the handling of personal data. However, India’s privacy Laws does not expressly define Sensitive Data. DPDP Act Applies to all the places with in the territory of India and processing of Digital Personal Data takes place overseas but offers it good and services in India. Some of the key factors which need introspection are as follows: · Protection of Personal Data to prevent data breaches using techniques like data isolations, Encryption and access Control. · Restricting the use of Customer Data to its stated Purpose. · Forbidding the retention of Personal Data when it is no longer needed · Impact on individual in case of Data Breach granting certain right to individuals over their Personal Data. · Granting certain Right to individual over their Personal Data. The LAW aimed to bring a balance between the Rights of the user and the need for the processing of Personal Data. DATA PRINCIPLE- A Person to whom the personal data relates, children and person with disability their parents a legal guardian. DATA FIDUCIARY– A person who controls the purpose and means of handling personal data like a small business, a startup or a bank. DATA PROCESSER– A person who handles processes data for the data fiduciary. SIGNIFICANT DATA FIDUCIARY– They may be designated by Central Government keeping in consideration factors like Volume and sensitivity of the data processed or Risk to National security and Electoral Democracy. LIST OF ENTITIES: 1. Individual 2. Hindu Joint Family 3. Company 4. Firm 5. Association of person may or may not be registered 6. The State as defines under the Article 12 of the Indian Constitution 7. Other Legal Person “The Act defines personal data as any data about an individual who is identifiable by or in relation to such data. “ Data Fiduciaries must implement necessary safety measures to prevent any data breach. It may include technical and organization measures comply with the obligation and other provisions. If the Government of India had issued any notification restricting the transfer of data to any other country or business must be complied with. Right of Data Principle: 1. Right to Access- They can request the detail. The details of all data fiduciaries and data processors with whom their personal data is shared. 2. Right to Correction– · Correct in any inaccuracies · Update their personal data · Complete their personal data Requests have to be fulfilled within reasonable time. 3. Right to Erase- The personal data can be deleted. 4. Right to Grievance Redressal- They resolve and issues regarding an act or commission of Data fiduciaries. Obligation or the enforcement of the data fiduciaries rights. Unless the data principle fails to get their grievance redress though this mechanism they can approach data protection board. 5. Right to Nominate- In the event of Death, Unsoundness of Mind or infirmity of Body. 6. Right to Revoke Consent- It can be revoked any time though they should bear any consequences arising from such revocation. Nature of violation/breach Penalty Failure to implement security safeguards Up to INR 250 crores (~ $30.213 million) Failure to notify a breach to the board Up to INR 200 crores (~ $24.17 million) Non-compliance with the special provisions regarding children Up to INR 200 crores (~ $24.17 million) Non-compliance with the obligations of SDF Up to INR 150 crores (~ $18.127 million ) Non-compliance of obligations by the data principals Up to INR 10,000 (~ $120) Violation of any voluntary undertaking if any Up to the extent applicable to that breach Violation of all other provisions than mentioned Up to INR 50 crore (~ $6 million) POWER AND OBLIGATION OF CENTRAL GOVERNMENT: 1. Without consent: If a processing is necessary or the performance of any function of the state authorized by Law like any service or benefit, issuance of permits and licenses. 2. Data Portability: The state has been exempted from the requirement to convert automated data in to structured, commonly used machine readable formats where processing is necessary. 3. Transfer of Sensitive & Critical Personal Data: Cross border transfer or sensitive personal data is possible when Central Government allows the Transfer of data to a country or an International organization. 4. Power of the Government exempt any Agency of Government: The Central Government can exempt any Govt. agency regarding a processing of specified personal data in the interest of Sovereignty and Integrity of India, Security of the state, friendly relation with the foreign stats and public order. In addition to this it can be granted from the grounds of preventing incitement to commit any cognizable offence. 5. Exemption of certain provisions: In the interest of prevention, detection, investigation and prosecution of the any offence for any other contravention of any law. 6. Exempt certain Data Processers: Central Govt. has the power of exemption to process the personal data of data principle not within the territory of India. 7. Issue Direction: The Central Government may issues direction Sovereignty and Integrity of India, Security of the state, friendly relation with the foreign stats and public order. KEY FEATURS: Applicability to Non- Citizens: The act applies to Indian residence and business collecting the data of India residence, non-citizen living in India whose data processing “In connection with any activity related to offering
DOES ELECTORAL BOND BONDS WITH DEMOCRACY?

World trends are changing every single day and that’s why the advertisement world needs to adapt to it fast
Corona Virus Vs Law

Corona Virus Vs Law Since the beginning of this year, the entire globe has been gripped byCovid- 19 and people at large are grappling with this pandemic while the Government had initiated a nationwide lockdown to curb and contain the widespread of this outbreak which has affected a substantial number of population. While this lockdown has helped contain community spread of the deceased a legal and legislation audit of this exercise has evaded scrutiny so far. The Disaster Management Act of 2005 was intended “to provide for the effective management of disasters and for matter connected therewith or incidental thereto”. Under this act, the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) was set up under the leadership of the Prime Minister and the National Executive Committee (NEA) was to be chaired by Home Secretary which laid out guidelines which establishments would be closed and which services suspended during the lockdown period. The State Governments on the other hand exercised powers under the Epidemic Diseases Act of 1897 to issue further direction like social distancing and isolation measures, strict home quarantine. However, the core issue remains to be answered whether the above-mentioned statutes were originally intended to or is sufficiently capable of addressing the grave threat of a pandemic. The use of the archaic Epidemic Diseases Act of 1897 reveals the lack of requisite diligence and responsiveness of Government authority in providing noble and innovating policy solutions to address 21-century problems. The colonial-era law arms the states with emergency power to carry out search operations as well as penalize people violating the provisions of law. The state has also invoked section 54 of the Disaster Management Act of 2005 to deal with people spread in fake news. :-“ whoever makes or circulates a false alarmed or warning as to disaster or its severity or magnitude, leading to panic, shall on conviction, be punished with imprisonment which may extend to 1 year or with fine. The Epidemic Diseases Act of 1897 does not provide any power to the Central Government to intervene in a biological emergency. Moreover, health is a state subject, and while the states are caught off guard, and their response also has been piecemeal. In order to meet the emergency situation like COVID 19, some countries have passed new statutes in order to meet the pandemic in the most efficient and effective manner. There is a realization in these countries that the prevailing provisions of the existing statutes are not sufficient enough to fight the biological emergency situation created by COVID 19. We can discuss one such example by the new Statute passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The Parliament of the United Kingdom passed the Corona Virus Act 2020 was by grants the government emergency power to handle COVID 19 pandemics. It has a time limit for two year It enables the government to restrict or prohibit the public gathering, control or suspend public transport, order business of such shops and Restaurants to be closed temporarily. Detained people suspected of COVID 19 infection. Suspend the operation of court temporally Close educational institutions and child premises Enroll medical students and retired health care workers in health services relax regulation to ease the burden on health care services. Assume control of death management in a particular local area. The Government has stated that these powers may be power switch on or off according to the medical advice it receives. The Act also provides for the measure to comeback the economic effect of the pandemic which includes the power the hold the eviction of tenants. Protect emergency volunteers from becoming unemployed and provide special insurance cover for health care staff taking on additional responsibility. The Government will also reimbursement of statutory sick pay for employees effected by COVID 19. Employers and supermarkets will be required to report supply chain disruption to the government. The Act formally postponed the local election and grants the UK the power to postponed and any other local election, local referendum. This act is subject to parliamentary renewal every six months. Therefore, we may conclude that though COVID 19 pandemic has led to actions being taken by the Government of India under the following Statutes like Epidemic Diseases Act of 1897 and the Disaster Management Act of 2005 unfortunately these Statutes have proved beyond doubt that they are not sufficient enough to meet the pandemic like situation in an effective and most efficient way. Therefore, we need a new tool in the form of a statute to meet this biological emergency whereby we can draw a new plan according to the prevailing situation. This will enable us to draw a new scheme of things which will not only help us in identifying the underlying problems relating to the field of social, economical, political, medical fields but will also prove to be an effective and efficient measure to control and eliminate the dreaded virus. Once the problem is identified the solutions will not be far. Therefore, a new plan in a form of a new Statute will enable both the Government and the citizens to come out of this grim situation and stand victorious in conquering the dreaded disease.
SURROGACY AND THE RIGHTS OF A SINGLE, UNMARRIED WOMAN

Of course, digital marketing agencies are adapting to the new changes that the world is going through.
MUSLIM WOMEN RIGHTS FOR MAINTAINANCE U/S 125 CrPC

MUSLIM WOMEN RIGHTS FOR MAINTAINANCE U/S 125 CrPC Section 125 CrPC requires a husband to support his wife (who is otherwise unable to maintain herself). It implies both interim and permanent maintenance and the word Social justice is justice in relation to a fair balance in the distribution of wealth, opportunities and privileges within a society where individual rights are recognized and protected for achieving equality and dignity of individual. Maintenance is recognized and accepted in legal parlance as a tool for social justice which is quantified in monetary terms to support the dependent. The right to maintenance is a statutory in nature and the dependents specially the wife can gain accessibility both under personal and secular laws. “wife” includes a divorced woman as well. The idea of maintenance is construed differently under different legislative laws but the goal is to provide assistance. In a Muslim man’s plea against direction to pay interim maintenance of Rs 20,000/- per month to his divorced wife. The Supreme Court is set to consider the question whether a Muslim woman is entitled to maintain a petition under Section 125 CrPC.This order was challenged before the Telangana High Court on the grounds that the parties got divorced in 2017 as per personal law. The divorce certificate was not recognized by the family court. The High Court reduced the quantum of interim maintenance to Rs 10,000/- p.m. to be paid from the date of petition. 50% of the arrears to be paid by January, 2024 and remaining 50% by March, 2024. The aggrieved petitioner approached the Supreme Court pleading that a divorced Muslim women is not entitled to maintenance u/s 125 CrPC. The petitioner urges that the provisions of Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Divorce) Act 1986 is more beneficial as a relief as far as maintenance is concerned. The petitioner claims that he has paid Rs 15,000/- as a maintenance during the iddat period and that the petitioner and his wife did not submit to any affidavit preferring CrPC over Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Divorce) Act 1986. The Supreme Court will consider the matter on February, 19, 2014. The Supreme Court in its landmark judgement pronounced and held that Section 125 CrPC is a secular provision applicable to Muslim women in Shah Bano Case. The same was nullified by Muslim Women (Protection of Rights on Divorce) Act 1986 and the validity of the law was held in 2001.
“EGG-CELLENT JUDGMENT”

“EGG-CELLENT JUDGMENT” Surrogacy is an arrangement in which a woman (the Surrogate) agrees to carry and give birth to a child on behalf of another person or couple (the indented parent(s)). She is also gestational carrier as she is a woman who conceives, carry and gives birth to a child for another person or a couple. Under the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act 2021, a woman who is a widow or a divorced between the age of 35-45 years or a couple defined as a legally married woman and man, can avail services of surrogacy if they have a medical condition necessitating this option. The Man shall be between the age of 26-55 years and the Woman between the aged of 25-50 years shall not have any previous biological, adopted or surrogate child. There is a ban on Commercial Surrogacy which is a punishable offence with a jail term of 10 years and a fine up to Rupees 10 Lakhs, so as to say that the Law only allows Altruistic Surrogacy where no money exchanged hand, where a surrogate mother is genetically related to those seeking a child. The Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation) Bill 2020 was introduced to regulate surrogacy procedures. The Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) refers to technique that seeks to obtain a pregnancy by handling a gamete (sperm/egg) outside the human body and transferring the gamete or fertilized embryo into the woman uterus. This arrangement includes In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) i.e. fertilizing an egg in the lab. Under the Surrogacy Act it is quite clear that another woman will bear a child for a couple or single women to be raised by the latter. The act in itself is very clear that surrogate offers to carry a baby through pregnancy and then return the baby to the intended parent(s) once it is born. Surrogacy is an option to fulfill the desire to have a child of a couple for whom it is physically or medically impossible or undesirable to carry a baby to turn own their own. There are three types of surrogacy- Traditional Surrogacy, Gestational Surrogacy and Altruistic Surrogacy. – In Traditional Surrogacy, a surrogate mother is artificially inseminated, either by the intended father or an anonymous donor. The surrogate mother provides the egg and is the genetically related to the child. – In Gestational Surrogacy, an embryo is created using an egg and sperm produced by the indented couple and is transferred in to the surrogate uterus. The surrogate has not genetic link to the child as her eggs are not used to conceive the child. Surrogacy can be altruistic or commercial. – In Altruistic Surrogacy the surrogate is not paid for her services except for medical expenses and insurance. The Surrogacy (Regulation) Bill seeks to ban Commercial Surrogacy where the surrogate is paid over and above the medical expenses and insurance. Opting for surrogacy is often a choice made by the woman who is unable to carry children on their own on account of abnormal uterus or absence of the uterus etc. Upon birth the child is legally recognized as the biological child of the intended couple. In a significant judgment Bombay High Court held that merely donating eggs or sperm by a person doesn’t entitled them to claim any parental rights on the child born through IN-Vitro Fertilization (IVF). Justice Milind Jadhav Pronounced the verdict by dismissing an argument of a woman, who (voluntarily) donated her OOCYTE (eggs for her sister). The court further clarified that the egg donor is a genetic mother but not a legal parent. The court has granted woman visitation rights to her 5 year old twin daughters, born through surrogacy. The petitioner, seeking visitation rights stating that her twin daughters lived with her strained Husband and her younger sister who had donated the eggs as Surrogate. Justice Milind Jadhav dismissed the claim and said further that the sister in law cannot be granted the status of the biological parent as her role was limited to being a voluntarily egg donor which her best can make her a genetic mother and not a legal parent. The High Court turns down the Lower Court decision which denied the Petitioner the visitations rights to her twin daughters. The Court has directed the husband to allow her physical access to the twins for 3 hours every weekend. Petitioner and her husband were legally wedded couple, but Petitioner failed to conceive naturally due to medical issues and after consulting a gynecologist it was diagnosed that the eggs of the Petitioner were non-viable. They were advised to ‘altruistic surrogacy’ through an egg donor and their after the Petitioner approached her younger sister to be the egg donor to which her sister agreed and both the parties entered in to a surrogacy agreement. Due to marital discord the Petitioner husband moved along with his daughters to his native place without informing the Petitioner as the Petitioner’s sister was in depression after the accident where she lost her husband and children, with the help of the support of their own parents she started residing with her brother in law and started taking care of his twin daughters. Petitioner filed a Police Complaint and an application seeking custody of her daughters under the provision of Guardian and Wards Act 1890 at District Court at Thane. The application was transferred to the Court of Ad-hoc District Judge Belapur, thereafter she files a interim application seeking visitation rights to her daughters which was rejected and there after she filed the present petition. The Court stated that under the National Guidelines of (Accreditation, Supervision and Regulation) ART clinics in India and the Surrogacy Agreement, it was clearly stated that the child born through ART shall be presumed to be the legitimate child of the couple as having been born from the wedlock and with the consent of both the spouses. – MAMTA SINGH SHUKLA (ADVOCATE DELHI HIGH COURT) MOBILE – 9560044035 Email Id: adv.mamtasinghshukla@gmail.com
Consumer Protection Act Vs Lawyers

Consumer Protection Act Vs Lawyers Consumer Protection Act Vs Lawyers Consumer Protection Law provides protection against issues like fraud, non-delivery of services, low quality of work in terms of product and services. The Consumer Protection Act 1986 was enacted to provide a simple and quicker access to redressal of consumer grievances. Now that the whole question revolves around if there was a deficiency in rendering services promised, for which the Lawyer received consideration in the form of a fee, then can the lawyers be proceeded against under Consumer Protection Act, 1986. In its 2007 judgement the Commission held that advocates do come under the purview of the Consumer Protection Act and can be dragged to a consumer court by their clients for deficiency in-service. The judgement declared that the legal services rendered by a Lawyers would come within the ambit of Section 2(1)(o) of the Consumer Protection Act 1986 that defines “service”, making them liable under the law Why can’t lawyers be sued for poor service if Doctors can be brought before consumer court for negligence? The Hon’ble Supreme Court raised this question whether a legal representative for a fee can be classified as a “service” under the Consumer Protection Act, 1986 Lawyers employ their skills and knowledge just like the Doctors does with his patients. So how it is different from a doctor?Undisputedly, Lawyers are rendering service and are charging the fee for the same. It cannot be clubbed under a contract for discharging personal service. Therefore, there is no reason to hold that they are not covered by the provisions of Consumer Protection Act, 1986, the Consumer Commission held in 2007 which was stayed by the apex Court in April 2009. Arguing on behalf of the Appellants, senior Counsel Narender Hooda objected to the rationale of the judgement of 2007 as lawyers stand on a completely different footing including the doctors. The first duty of a lawyer is towards the court since he has to act as an officer of the court. There is no one to one relationship that a lawyer has with his clients and success of a case does not depend only on the skills of a lawyer but on the court itself. Disagreeing to this argument bench said if a lawyer does not remain present in the court and an ex-parte decree is passed and the lawyer does not even bother to inform his client, this tantamount to sheer negligence in service. To this argument Senior Counsel said that there is already a mechanism under the Advocates Act to conduct an inquiry against the lawyers for misconduct. Negligence and misconduct are two different concepts and moreover there are regulations under Medical Council Of India but still the doctors come under the ambit of Consumer Protection Act the Bench said. Bench further said that the court can always decide and adjudicate whether it is professional misconduct or negligence. Court has further held how lawyers and doctors are different in providing services.
EMOJI STATUTARY CONSTRUCTION
EMOJI STATUTARY CONSTRUCTION Emoji has been derived from the Japanese word meaning “picture character”. Oxford dictionary defines Emoji as a “small digital image or an icon used to express an idea, emotion etc. in electronic communication”. Unlike plain text where people view the same character in their exchange platforms effectively translate Emoji. The Emoji that a sender chooses is translated to the receiver’s platform rendering since Emoji renders differently on different platforms. The emoji graphic that is send by one person on one device may be quite different than what is seen by the recipient using a different device. Non-Unicode Emojis are usually not compatible across multi-level platforms, so the recipient on the other platforms will see a placeholder symbol replacing a non-Unicode Emoji or nothing at all. JUDICIAL INTERPRETATION OF EMOJI- VISUAL DECODING-this brings us to the question of visual decoding, very often the small size of Emoji makes them difficult to decode as many a times subtle differences are difficult to distinguish, mistaken decoding can lead to misinterpretation. SYMBOLS MAY HAVE MULTIPLE MEANINGS – Similarly, many symbols may have multiple meanings which may add ambiguity to the messages which can be interpreted in several ways e.g. folded hands Emoji convey thank you or I am praying. This poses a special problem because there is no definitive reference source catalogue. Though Unicode provides a short description of every Emoji but at the same time it acknowledges that it may not encompass all the possible meanings. CULTURAL DIFFERENCE –Then again if there is a cultural difference between the sender and the recipient misunderstandings are likely to follow. Proper Emoji evidence is before the interpreter then the whole matter becomes a part of applicable substantive law. Over a period of time Emoji’s usage has increased many fold, it is away to express ourselves. Though it is a general perception that Emoji’s are for the sake of fun and are cute in nature but there usage are leading to misunderstanding in legal interpretation for example whether someone is liable for Sexual Harassment or obligated by Contract. We all are witness to the fact that our legal system has evolved substantially in interpreting new forms of contents. Those it holds true to handle Emoji’s or it means extra interpretive challenges. Over the ages we are also witness to the fact that the mode of communication evolved with technological advancement, the symbols of communications which serve as visual representation to express any information, emotions or ideas. In the recent times Emoji’s has led to legal disputes and had to be interpreted based on various interpretation in different jurisdictions. INTERNATIONAL PRESPECTIVE ON THE USAGE OF EMOJI CANADA: South West Terminal Ltd. Vs. ACHTER Land and Cattle Ltd. – The Court was concerned with the question of whether there was a valid Contract between the buyer and the seller. The buyer subsequent to a conversation on mobile sign the Contract and then took a photo of it using his cell phone and send it to the seller with the message “ Please confirm FLAX Contract” the Seller texted back a “Thumps Up”( 👍 ). It was contented on behalf of the seller that the Emoji meant a sort of acknowledgement of receiving the message while the purchaser said it was meant to be for the affirmation of the Contract. While adjudicating the case Justice “Keene” looked in to the dictionary for the meaning of “Thumps up” ( 👍 ), -it is used to express assent, approval or engagement in digital communication and the court found that there was consensuses-ad-idem between the buyer and the seller and that the Contract was enforceable. The seller was asked to pay damages for the Breach of the Contract. U.S.A Emoji’s are increasingly appearing in criminal cases in U.S.A. and there use can significantly impact how evidence is interpreted and understood. In the Trial of Ross Ulvriched the founder of silk road online market place was convicted of Money Laundering , Computer Hacking and Conspiracy in this case all internet communications including Emoji’s was considered by the Jury while deliberating the intention of the accused. So the Emoji’s can be submitted as evidence in the court with their admissibility to contingent on relevance to the case and their accuracy of their interpretation within the communication context. FRANCE: Azougagh Bilal was convicted for making criminal threats by sending a gun shaped character to his Ex-Girlfriend through a text message sent from his Mobile Number the court found that the the message constituted a death threat in the form of an image which determines his intent Men’s-Rea .He was sentence to 6 months of imprisonment and a 1000 Euro fine. ISRAELI: Dahan Versus Shakaroff.-The Judge observed that the positive Emoji’s which included a smiley face(J), a bottle of champagne, Dancing figure indicated and intent to do business and awarded damages to the land lord. AUSTRALIA: In Burrows Vs Houda, Houda a Lawyer reposted a tweet about an another Lawyer Burrow, the plaintiff who was facing disciplinary action from the Law Society due to alleged misconduct. The inclusion of the Zipper mouth was held to be defamatory. The Judge relaying on online dictionary Emoji-pedia said that in meant a ‘secret’, ‘Stop talking’ the court observed the post was easily accessible to the Twitter user which would result in considerable harm to Burrows reputation which would affect her carrier as a Lawyer. INDIA: Director General, Railway Protection Force Vs. Narendra Chauhan. In this Narendra Chauhan was an employee of the Central Railway Protection Special Force was dismissed from service for putting a “thums up” ( 👍 ) as a reply to a message in a WhatsApp group were a video of a constable murdering the assistant commander was shared. This was construed as he was giving a morale support to the accused and was celebrating the Murder. Disciplinary proceeding was conducted and he was removed from service over his Emoji remark. The division bench of the Madurai bench of Madras High Court considered the “thums up” ( 👍 ) Emoji to be construct to be an alternative to the word “OK” it further said that sharing of Emoji Symbol did not amount
Client or Consumer?

Client or Consumer? A bench comprising of Justices Bela M Trivedi and Pankaj Mittal said the legal profession is Sui generis (unique) where the nature of work is specialized and cannot be compared with other professions on the question of whether the lawyers be sued under Consumer Protection Act. It was held that the success of ‘Professionals’ often depends on factors outside their control and client cannot take legal action against their lawyers by claiming that they did not provide proper ‘Service’ as per The Consumer Protection Act 1986, (CPA). The Supreme Court decision in Indian Medical Association v/s V.P Shantha, 1995, stated that the services by the medical practitioners would fall under CPA. The National Consumer Disputes Redressal’s (NCDRC) decision in this was held that the Lawyers’ Services fall under the definition provided for the term U/S 2 (O), of The Consumer Protection Act, 1986 (CPA). If there is any deficiency in the service the NCDRC held that complain could be filled under CPA. Ruling of the Apex Court: The Supreme Court distinguished between the terms ‘Business’ or ‘Trade’ and ‘Profession’. The Apex court reiterated that Business or Trade have Commercial connotation and cannot be used interchangeably with the term Profession. Advocates have to respect Clients autonomy and are not entitled to make concessions without express instruction from client and there is a considerable amount of direct control of advocates with the clients. The contract is not a contract in the strict terms but the nature of service which is provided can safely by termed ‘personal service’. Therefore it can be excluded from the definition under CPA. The reason for this is that the Lawyers follow their client’s instructions and cannot make decisions at their own instance; it makes the legal contract personal in nature. The Terms ‘Service’ is defined very broadly under the CPA but excludes Free Services and contracts of personal service. The Lawyers render service and charged the fee for it which is a basic requirement of the term ‘Service’ under CPA 1986. Though, it is necessary to point out that a lawyer may not be held responsible for the outcome of the case but surly he is responsible for deficiency in rendering the promised services. Further, it can be inferred that deficiency in the services must be considered under the lens whether it is preformed negligently or deficiently. It cannot be viewed on the basis of the cases which are lost, otherwise it would give the right to the client to sue their lawyers. Section 2 (1) (g) of CPA defines the ‘Deficiency in Service’- it must be in relation to and always in term of service which the advocate provided to the client. Thereby indicating that if the grievance pertains to the matter which does not fall in the definition of Service section 2(1) (O), the concept of deficiency would not apply. So as to say that the advocate would not be liable to the client under CPA 1986. Conclusion: The Apex Court ruled that the advocates are not liable for deficiency of services under the Consumer Protection Act 1986, and therefore cannot be sued for poor service before the consumer courts. The Lawyers can only be tried for Professional Misconduct. Professional Misconduct is any action that puts the Advocate in conflict with their profession or rendered them unfits to practice. Professional Misconduct includes the following: Betraying the trust of the client. Practicing fraud through certain means. Deceiving the court. Deceiving the opposing party or their counsel. Improper or Inappropriate behavior. Behavior that is unlawful according to law. Immorality. Carelessness in discharge of duties. An Act forbidden by Law. Transgression. All though the Bar Counsel of India and the BCI Act do not specifically define Professional Misconduct but serious penalties has been established for any registered advocate who commits or falls to commits such an Act. – MAMTA SINGH SHUKLA (ADVOCATE DELHI HIGH COURT) MOBILE – 9560044035 Email Id: adv.mamtasinghshukla@gmail.com

